Pareto analysis is a really useful technique used to determine the most influential factors in a situation. It can be used to improve your organisation by identifying where you can make the most impact with your time and resources or to address problems in a hierarchy of order of most critical.
1: What is the Pareto Principle or the 80/20 Rule?
The pareto concept was created by Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto where he observed that 80% of the land in Italy was owned by 20% of the population. This led him to develop the pareto principle, whereby 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes. This principle is used to help identify which elements are most important in a given situation. In other words, if you look at something from a broad perspective, it’s likely that most things follow the pareto principle. For example, 80% of road accidents might be caused by 20% of the drivers in a certain area or 80% of income is generated by 20% of your client base or 80% of defects and returns come from 20% of products being sold.
By understanding this rule, decision makers can focus their efforts on the most important items and address them first, driving the most value from time and resource allocation.
2: How to use Pareto Analysis in your Organisation ?
It works by helping to identify the most critical issues from a larger set of data. To use Pareto Analysis, first, you need to collect data that is relevant to the problem you are trying to solve. Then, use the data to create a Pareto chart which displays the most important factors that are causing or contributing to the problem.
Next, prioritise the factors on the chart in order of importance so that you can focus on those that will have the biggest impact. Once you have identified the most important factors, you can then take action to address them. This could include making changes to processes or procedures, or taking steps to reduce or eliminate certain factors altogether. By using Pareto Analysis, decision makers can quickly identify and address problems more efficiently and effectively and drive greater customer satisfaction, employee engagement and improved financial results.
3: How to construct a Pareto Chart?
1. Define the problem
2. Identify the possible causes of the problem
3. Collect then record the data
4. Calculate the frequencies of the identified causes
5. Draw a vertical bar for each cause or cause group
6. Sort them by frequency in descending order
7. Calculate then draw the cumulative percentage line
8. If you observe a Pareto effect, focus your improvement efforts on those few factors to get the most effective outcome
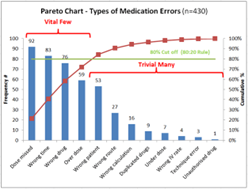
For any problem solving culture, Pareto is a must-know. By understanding and using the 80/20 rule in your organisation, you can make meaningful progress towards achieving your goals.
CI Teams are experts in assisting organisations with Lean and Continuous Improvement. If your organisation needs assistance in learning the tools of Lean and implementing a continuous improvement culture, feel free to contact us.

